A
Acute Angle: An angle with a measure less than 90º
Addend: Any number that is being added.
Analog Time: Time displayed on a timepiece having hour and minute hands.
Area: The measure, in square units, of the inside of a plane figure.
Array: A rectangular arrangement of objects in equal rows or columns.
B
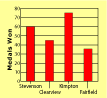
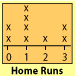
Bar Graph : A graph that uses bars to show data.
C
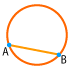
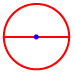
Chord: A line segment whose endpoints are on a circle.
Circumference: The distance around a circle.
Combination: A group of items. Placing these items in a different order does not create a new combination.
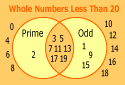
Composite number: A whole number having more than two factors.
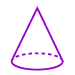
Cone: A solid figure that has a circular base and one vertex.
Congruent: Having the same size and shape. EXAMPLE - Congruent angles have the same measure; congruent segments have the same length.
Cube: (noun) A rectangular solid having six congruent, square faces.
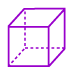
Cube: (verb) To raise a quantity or number to the third power. (x)(x)(x)
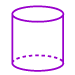
Cylinder: A three-dimensional figure with two circular bases, which are parallel and congruent.
D
Diameter: A line segment that has endpoints on a circle and passes through the center of the circle.
Difference: The answer in a subtraction problem. EXAMPLE: 8 - 3 = 5; 5 is the difference.
E
Edge: The line segment where two faces of a solid figure meet.
Equation: A statement that two mathematical expressions are equal.
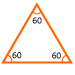
Equilateral triangle: A triangle with all three sides of equal length. The angles of an equilateral triangle are always 60°
Equivalent: Having the same value.
Expanded notation: A way to write numbers that shows the value of each digit
(EXAMPLE: 4372 = 4000+300+70+2).
Expression: A variable, or any combination of numbers, variables, and symbols that represents a mathematical relationship (EXAMPLE: 24 x 2 + 5 or 4a – 9).
F
Face: A plane figure that serves as one side of a solid figure.
Fact family: A set of related addition and subtraction, or multiplication and division equations using the same numbers (EXAMPLE: 6+9=15, 15-9=6, 9+6=15, 15-6=9).
Factor: A whole number that divides evenly into another whole number (EXAMPLE: 1, 3, 5, and 15 are factors of 15).
Function: A relation in which every input value has a unique output value.
G
Greatest common factor (GCF): The largest factor that 2 or more numbers have in common.
H
Heptagon: A polygon with 7 sides.
Hexagon: A polygon with 6 sides.
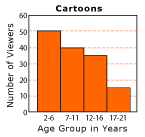
Histogram: A bar graph in which the labels for the bars are numerical intervals.
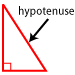
Hypotenuse: The longest side of a right triangle (which is also the side opposite the right angle).
I
Inequality: A mathematical sentence that contains a symbol that shows the terms on either side of the symbol are unequal (EXAMPLE: 3+4>6).
Intersecting lines: Lines that cross.
Irrational Number: a number that cannot be written as a simple fraction - it's decimal goes on forever without repeating. It is called "irrational" because it cannot be written as a ratio (or fraction).
Isosceles triangle: A triangle with two equal sides.
L
Least common denominator (LCD): The least common multiple of the denominators in two or more fractions.
Least common multiple (LCM): The smallest number, other than zero, that is a common multiple of two or more numbers.
Leg (of a right triangle): Either of the two sides that form the right angle in a right triangle.
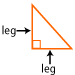
Line: A straight path extending in both directions with no endpoints.
![]()
Line of symmetry: A line that divides a figure into two halves that are mirror images of each other.
Line plot: A graph showing the frequency of data on a number line.
Line segment: A part of a line with two endpoints.
![]()
M
Mean (average): The number found by dividing the sum of a set of numbers by the number of addends.
Median: The middle number in an ordered set of data, or the average of the two middle numbers when the set has two middle numbers.
Mode: The number(s) that occurs most often in a set of data.
Multiples: The product of a given whole number and another whole number (EXAMPLE: multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16….).
N
Nonagon: A polygon with 9 sides.
Number sentence: An equation or inequality with numbers.
O
Obtuse angle: An angle with a measure more than 90º.
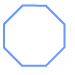
Octagon: A polygon with 8 sides.
Ordered pair: A pair of numbers used to locate a point on a coordinate grid. The first number tells how far to move horizontally, and the second number tells how far to move vertically.
P
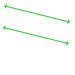
Parallel lines: Lines that never intersect and are always the same distance apart.
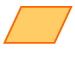
Parallelogram: A quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
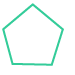
Pentagon: A polygon with 5 sides.
Perimeter: The distance around a figure.
Permutation: The action of changing the arrangement, especially the linear order, of a set of items.
Perpendicular lines: Two lines, segments or rays that intersect to form right angles.
Pictograph: A graph that uses pictures to show and compare information.
Plane: A flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions.
Prime number: A whole number that has exactly two factors, 1 and itself.
Product: The answer to a multiplication problem. EXAMPLE: 6 x 2 = 12; the product is 12.
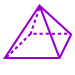
Pyramid: A solid figure with a polygon base and triangular sides that meet at a single point (vertex).
Q
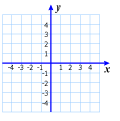
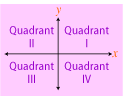
Quadrants: The four regions of a coordinate plane that are separated by the axes.
Quadrilateral: A polygon with 4 sides.
R
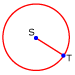
Radius: A line segment that has one endpoint on a circle and the other endpoint at the center of the circle.
Range: The difference between the greatest and least numbers in a set of data.
Rate: A ratio that compares two quantities having different units (EXAMPLE: 95 miles in 2 hours).
Ratio: A comparison of two numbers using division.
Ray: A part of a line that has one endpoint and continues without end in one direction.
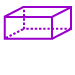
Rectangular prism: A solid figure in which all six faces are rectangles.
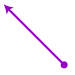
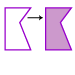
Reflection (flip): A transformation that produces the mirror image of a figure.
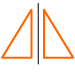
Regular polygon: A polygon that has all sides congruent and all angles congruent.
Remainder: The amount left over when a number cannot be divided equally.
Repeating decimal: A decimal that has a repeating sequence of numbers after the decimal point.
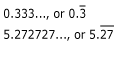
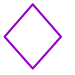
Rhombus: A parallelogram with four equal sides.
Right angle: An angle that measures exactly 90º.
Right triangle: A triangle that has a 90º angle.
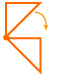
Rotation (turn): A movement of a figure that turns that figure around a fixed point.
S
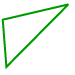
Scalene triangle: A triangle in which no sides are equal.
Similar polygons: Polygons that have the same shape, but not necessarily the same size. Corresponding sides of similar polygons are proportional.
Sphere: A solid figure that has all points the same distance from the center.
Square: (noun) A 4-sided polygon where all sides have equal length and every angle is a right angle (90°).
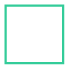
Square: (verb) To rasie a number or quantity to the second power. (The number is multiplied by itself.) (x)(x)
Straight angle: An angle with a measure of 180º.
Sum: The answer to an addition problem. EXAMPLE: 12 + 7 = 19; the sum is 19.
T
Tally chart: A table that uses tally marks to record data.
Terminating decimal: A decimal that contains a finite number of digits.
Tessellate: To combine plane figures so that they cover an area without any gaps or overlaps.
Transformation: The moving of a figure by a translation (slide), rotation (turn) or reflection (flip).
Translation (slide): A movement of a figure to a new position without turning or flipping it.
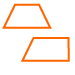
Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides.
U
Unit price: The price of a single item or amount (EXAMPLE: $3.50 per pound).
Unit rate: A rate with the second term being one unit (EXAMPLE: 50 mi/gal, 4.5 km/sec).
V
Variable: A letter or symbol that stands for a number or numbers.
Venn diagram: A diagram that shows relationships among sets of objects.
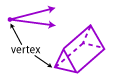
Vertex: A point where lines, rays, sides of a polygon or edges of a polyhedron meet (corner).
Volume (capacity): The amount of space (in cubic units) that a solid figure can hold.
W
Whole number: Any of the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … (and so on).
X
X-axis: The horizontal number line on a coordinate plane.
Y
Y-axis: The vertical number line on a coordinate plane.